Market research
If you want to conduct a survey or a more in-depth study, you will often go to the Research methodology asked. How do you answer?
There are many methods you can use and this article will help you find the right method and choose the one that is best suited to answer your research question.
CONTENT
- 1 What is a research methodology?
- 2 How to choose the right research methodology?
- 3 What is qualitative, quantitative and mixed research methodology?
- 4 How is a sampling plan created?
- 5 Main methods of data collection
- 6 What are the main methods of data analysis?
- 7 How to Write a Research Methodology
- 8 1:1 Live Online Presentation: QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
- 9 Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
What is a research methodology?
Research methodology simply means how a researcher systematically designs a study to ensure valid and reliable results that meet the objectives of the research.
Research methodology is the method you use to solve a research problem by collecting data using various techniques, interpreting the collected data, and drawing conclusions from the research data. Essentially, research methodology is the blueprint for a research or study.
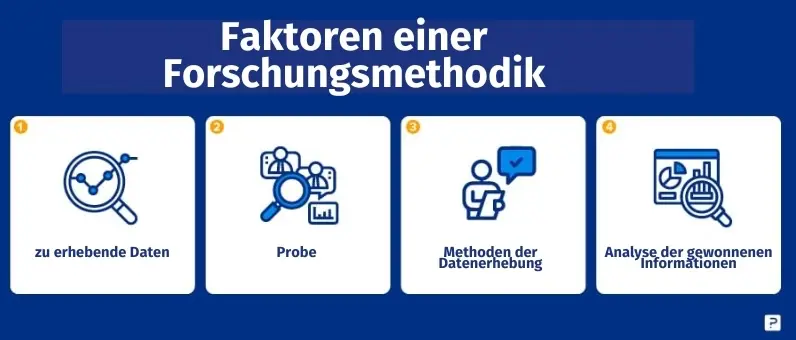
To achieve this, you must consider the following factors, among others:
- What data you collect (and what you ignore).
- who you commission to collect data (in research this is called “Sampling plan" designated)
- how the data is collected (this is referred to as “Data collection methods" designated)
- how to analyse the data (this is called “Data analysis methods" designated)
In a formal study, you will find a chapter (or section) on research methodology that covers the aspects mentioned above. It is important that a good methodology explains not only what methodological decisions were made, but also why they were made.
In other words, if you know what methodology you used, you can Research design justify it by showing that the chosen methods and techniques meet the objectives of the research, and also mention that they will produce results and why they will be valid and reliable.
A good research methodology produces scientifically sound results, whereas a bad methodology does not.
How to choose the right research methodology?
The goals of your research have a major impact on the research methodology. The starting point for developing research methodology is therefore to take a step back and look at the bigger picture of the research before making methodological decisions. The first question to ask is whether the research is exploratory or confirmatory.
If the objectives of the research are primarily exploratory, it is likely that you will need to conduct qualitative research and therefore use qualitative data collection methods, e.g. B. Interviews and qualitative content analysis methods can be considered.
On the other hand, if the goals of your research are to measure or prove something (i.e. confirmatory), you should choose quantitative research and consider quantitative data collection methods, such as: B. Surveys and statistical analysis.
Most importantly, always start with the objectives of the research paper. All methodological decisions arise from this.
What is qualitative, quantitative and mixed research methodology?
Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed research methodology are different types of methodology that differ in that they focus on words, numbers, or both. This is a gross oversimplification, but a good starting point for understanding.
Qualitative research refers to research that focuses on the collection and analysis of words (written or spoken) and textual data, while quantitative research focuses on measurement and testing using numerical data. Qualitative analysis can also focus on other “softer” data, such as body language or visual elements.
It is common to use a qualitative methodology when the research objectives are exploratory in nature. For example, a qualitative methodology can be used to learn people's perceptions of an event or a presidential candidate.
In contrast, a quantitative methodology is typically used when the research objectives are confirmatory in nature. For example, a quantitative method can be used to measure the relationship between two variables (e.g. personality type and likelihood of committing a crime) or to test a series of hypotheses.
As you have probably guessed, mixed methods methodology attempts to combine the best of qualitative and quantitative methods to integrate perspectives and create a comprehensive picture of the data.
How is a sampling plan created?
The sampling plan is one of the phases of the research methodology and consists of deciding what the sample should be. There are many ways to select a sample, but the two main categories of sampling plan are probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling is a random sample of the group of people you are interested in (this group is called the “population”). Using a completely random sample generalizes the results of your study to the entire population.
In other words, you can expect the same results across the entire group without having to collect data from the entire group (which is typically not possible with large groups).
In contrast, non-probability sampling does not use a random sample. For example, a random sample can be used, which means surveying people you have access to (e.g. friends, family, or work colleagues), rather than creating a true random sample (which can be difficult due to resource limitations). With non-random samples, the results are usually not general.
Main methods of data collection
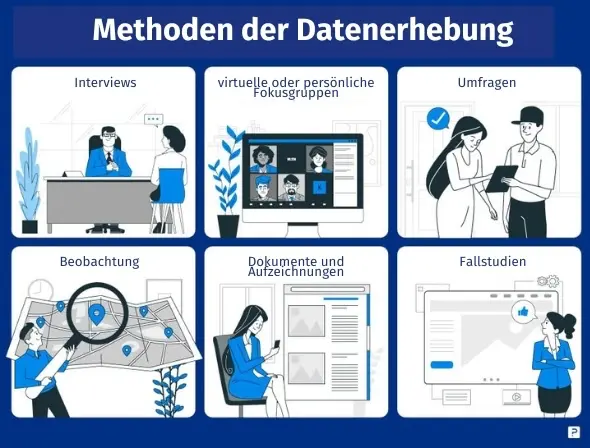
There are many data collection methods you can use for your study. However, these options can be divided into the following types:
- Structured, semi-structured and unstructured interviews.
- Virtual or in-person focus groups
- Online or physical surveys
- Observation
- Documents and records
- Case studies
The choice of data collection method depends on the general research objectives as well as practical considerations and resource limitations.
For example, if your research is exploratory in nature, qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups are probably most appropriate. On the other hand, if your research aims to measure specific variables or test hypotheses, large-scale surveys that provide large amounts of numerical data are probably more appropriate.
Platforms such as online communities allow you to use both qualitative and quantitative methods.
What are the main methods of data analysis?
Another important part of the research methodology is data analysis. Data analysis methods can be divided into groups depending on whether the research is qualitative or quantitative.
The most common data analysis methods in qualitative research are the following:
- Qualitative analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Grounded theory
- Analysis of significance assessment
Qualitative data analysis begins with coding the data, after which one (or more) analysis techniques are applied.
The most common methods of data analysis in quantitative research are the following:
- Descriptive statistics (eg Mean, median and mode).
- Inferential statistics (e.g., correlation analysis, regression analysis, structural equation modeling).
Again, the choice of data collection method depends on the general research objectives as well as practical circumstances and resource limitations.
How to Write a Research Methodology
This guide is intended to help you organize your research methodology:
- Present your methods. Introduce the methodological approach you will use, whether quantitative, qualitative or mixed.
- Establish the methodological context. This means that you must explain why your methodology is suitable for achieving the goal of your research. Remember that the connection between your methods and your research problem must be clear.
- Introduce your research tools. Specify which tools you will use to collect your data and explain how you will use them. These tools can be surveys, interview questionnaires, observations, etc. If your methods involve archival research or analysis of existing data, provide background information on the documents.
- Present your analysis. Explain how you will analyse the research data to support your explanation of the results obtained.
- Share the sampling procedure. Explain why you chose one type of sampling. For example, if you conduct interviews, describe how you will select participants and how the interviews will be conducted.
- Address the limitations of the investigation. Make sure your research report addresses potential limitations you may encounter in your research, as well as limitations that may impact your data collection process.
These were some recommendations for the research methodology you will use. However, there are some factors you should avoid:
- Don't provide irrelevant details.
- Details that do not contribute to understanding your chosen methods should not be included in the methodology section.
- Irrelevant information also includes unnecessary explanations of basic procedures. Basic procedures should only be explained if they are unconventional and unfamiliar to readers.
- Don't ignore the problems that may arise during data collection.
Remember that QuestionPro has a number of tools to help you with your next research methodology. Learn the features of our survey software and start preparing your next study today!
1:1 live online presentation:
QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
Arrange an individual appointment and discover our market research software.
Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
Do you have any questions about the content of this blog? Simply contact us via contact form. We look forward to a dialogue with you! You too can test QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge and without risk in depth!
Test the agile market research and experience management platform for qualitative and quantitative data collection and data analysis from QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge
FURTHER KEYWORDS
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
KEYWORDS OF THIS BLOG POST
Research methodology | Research | Methodology
FURTHER INFORMATION
- Research Synthesis: Understand your research results
- Synthetic data: what they are, types, methods and uses
- Research Process: Steps to conduct the research
- Synthetic data generation: techniques and perspective
- Digital behavioral data: what it is, its importance and risks
- Data filtering: what it is, benefits and examples
- Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: Which is Better?
- Big Data and Artificial Intelligence: How do they work together?